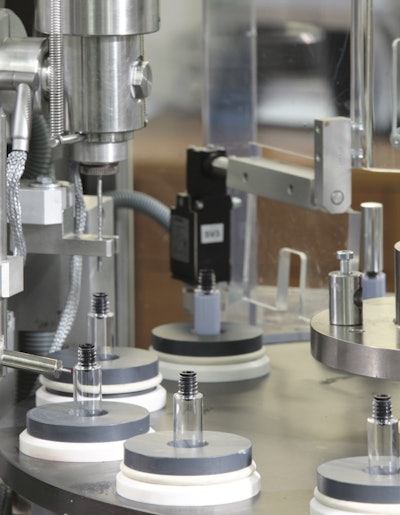
In addition to a high initial capital investment, one complexity of the pharmaceutical industry is the strict regulatory controls that make the sector challenging to thrive in and largely dominated by multinationals that have the resources to meet these requirements.
Manufacturers face many challenges with implementation, such as replacing legacy systems throughout the supply chain that are often inadequate for processing the large volume of data necessary for compliance. Additionally, the cost of meeting these standards is high, with some reporting that they have already invested upwards of $50 million on building the necessary capabilities for compliance.
-
The European Union Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) outlines measures which include the need for serialization of packages to enable traceability of drugs throughout the supply chain. This includes the mandate that packaging must include 2D codes. The deadline for meeting the FMD legislation has been extended from the start of 2017 to the start of 2019 to allow companies to fully implement and comply. Despite Brexit, the United Kingdom still plans to comply with this legislation.
-
In Brazil, RDC 54, according to law 13.140/16, there will be several implementation deadlines leading up to the 2021 deadline requiring all products to be serialized and traced. Legislation around traceability is largely affecting this sector and is driving the labeling, coding and decorating machinery market to be one of the fastest growing.
-
The China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) has been gradually implementing its Electronic Drug Monitoring Network since 2011, which is part of its plans to enable traceability of all drug products through the supply chain. In July 2016, the CFDA released an update that it would be revising the pharmaceutical quality management specification, alluding to future serialization requirements.
Source: PMMI Business Intelligence, “Global Trends Impacting the Market for Packaging Machinery 2018.” Download the FREE full report here.